Basic Concepts
Introduction
Electric Circuit Theory & Electromagnetic Theory are the
two fundamental theories upon which all branches of electrical engineering are
built.
Our objective in this article is not the study of various
uses and applications of circuits. Rather our major concern is the analysis of
the circuits. By analysis of a circuit we mean study of the behavior of the
circuit: How does it respond to a given input? How do the interconnected elements
and devices in the circuit interact?
We
will be using the International System of Units (SI), adopted by the General
Conference on Weights and Measures in 1960.
Electric Charge and Current
Electric Charge is the property of matter by virtue of which it
responds to an electromagnetic field. Charge is measured in Coulomb.
Charge is Quantized: The only charges that occur in nature are integral multiples of the electronic charge

The law of conservation of charge states that charge can neither be
created nor destroyed, only transferred. Thus the algebraic sum of the electric
charges in a system does not change.
Electric
Current is the time rate of change of charge, measured in Ampere (A).
1 Ampere=1 Coulomb/second
A direct current (dc) is a current that remains constant with time.
Alternating
Current is a current that varies with time.
Voltage or
Potential Difference
The
voltage
between two points in an electric circuit is
the energy (or work) needed to move a unit charge from a to b; mathematically,
Where w is energy in Joules
(J) and q in coulombs (C).
Polarity of Voltage
The (+) and (–) signs are used
to define reference direction or voltage polarity.
Polarity
of Voltage
The
common term signal is used for an electric quantity such as a current or
voltage (or electromagnetic wave) when it is used for conveying information.
Power and
Energy
Power is the time rate of
expending or absorbing energy. Power is measured in Watt (W).
If
current leaves from the +ve terminal of an element then the element is
delivering power and if the current enters the +ve terminal of an element then
the element is absorbing power.
Associated
Variable Convention
1) Active Sign Convention: If the current
leaves from the +ve terminal of an element
and if the
current enters the +ve terminal of an element p = -vi.
2) Passive Sign Convention: If the current
leaves from the +ve terminal of an element
and if the
current enters the +ve terminal of an element p = +vi.
We use Active Sign Convention: If the
element delivers power (or energy) then the power is taken +ve
else the power
is taken –ve.
The
law of conservation of energy must be obeyed in any electric circuit.
Consequently, the algebraic sum of power in a circuit at any instant of time
is zero.
Energy
is
the capacity to do work, measured in Joule (J).
Circuit
Elements
There are two types of
elements: Active Elements and Passive Elements.
An active element is one that
can generate energy and a passive element is one that can’t generate energy. So
Passive elements include resistor, capacitor & inductor & Active
elements include op-amps, BJT, current source, voltage source etc.
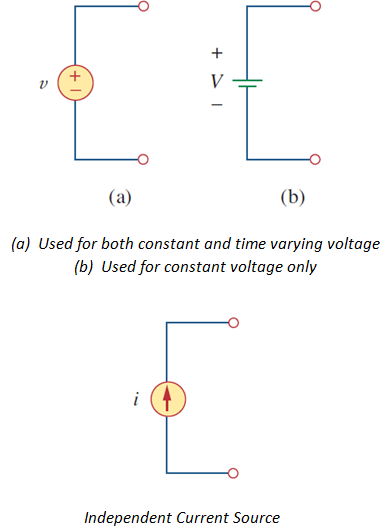
There are two kinds of
sources: Independent Sources and Dependent Sources.
An ideal independent source is
an active element that provides a specified voltage or current that is
independent of other circuit elements.
Following
pictures show the symbols used:
An ideal dependent source is
an active element in which the source quantity is controlled by another voltage
or current.
1) VCVS
– Voltage Controlled Voltage Source
2) VCCS
– Voltage Controlled Current Source
3) CCVS-
Current Controlled Voltage Source
4) CCCS-
Current Controlled Current Source
Following pictures show the symbols used:
A note to the reader: In the
next article I will be covering the Basic Laws including Ohms Law,
Kirchhoff’s Laws, Combination of Cells and resistors, Voltage Division &
Current Division.
For any questions or queries feel free to contact: abhisekroutwrites@gmail.com














Comments
Post a Comment